A well-defined Vision, Mission, and Values (VMV) statement is the foundation of our marketing strategy. These components provide us with guidelines to make the right organizational decisions and inspire employees to work for a shared objective.
Yet, it’s common to see new businesses frustrated and struggling to write their VMV statements since we have no universal definition of each of them.
This typically results in generic platitudes that fail to inspire or differentiate. Organizations lose their competitive edge because of the lack of shared values among employees, making them fail to connect with the target audience.
In this blog article, we will discuss the principles of vision, mission, and values and build an insightful guideline to help you create authentic and actional VMV statements that drive your businesses to succeed.
Read More: Leverage Serial Position Effect To Upgrade Marketing Strategy
Understanding Vision, Mission, and Values
1. Vision
Vision is what a company wants to achieve or become in the future. It is the organization’s aspirational image that serves as a guiding light for strategic decision-making.
Having a clear vision statement provides the employees with a look ahead into the desired state of the company in the future. It guides employees towards a common goal and fosters enthusiasm for innovation and growth.
Failing to understand or craft a clear vision statement can lead to a lack of direction, decreased employee motivation, and difficulty in adapting to market changes.
Some characteristics of a perfect vision statement, suggested by Dr. Shelley A. Kirkpatrick, include:
- Clarity: how well the employees understand and feel driven by it.
- Future focus: clearly describe the company’s desired state in the future.
- Abstractness and challenge: understand the challenges of the current situation and the opportunities to reach the future state.
- Idealism: a highly desirable and attainable future.
- Brevity: concise and easy to remember.
- Uniqueness: showcase how the company differentiates itself from other organizations.
- Success definition: stating how the company measures its progress in achieving the desirable future.
Examples of Great Vision Statements:
Coca-Cola – “Our vision is to craft the brands and choice of drinks that people love, to refresh them in body & spirit. And done in ways that create a more sustainable business and better-shared future that makes a difference in people’s lives, communities, and our planet.”
Amazon – “Our vision is to be earth’s most customer-centric company; to build a place where people can come to find and discover anything they might want to buy online.”
Nike – “We see a world where everybody is an athlete — united in the joy of movement. Driven by our passion for sport and our instinct for innovation, we aim to bring inspiration to every athlete in the world and to make sport a daily habit.”
Tesla – “To become the most attractive automobile company of the twenty-first century by spearheading the world’s shift to electric vehicles.”
2. Mission
The mission is the foundational purpose and guiding principle for daily operations. It explains the organization’s reason for existence and its primary objectives besides profit.
Experts say a mission statement should address key questions about the firm’s purpose, distinctive competencies, target market, and desired position in the industry.
The mission should resonate with stakeholders’ values and expectations to inspire dedication and action in the organization’s interest. It typically incorporates organizational values, which should be reflected in the company’s code of ethics and culture.
Examples of Great Mission Statements:
Toyota – “Through our commitment to quality, ceaseless innovation, and respect for the planet, we strive to exceed expectations and be rewarded with a smile.”
Disney – “To entertain, inform, and inspire people around the globe through the power of unparalleled storytelling, reflecting the iconic brands, creative minds, and innovative technologies that make ours the world’s premier entertainment company.”
IKEA – “to offer a wide range of well-designed, functional home furnishing products at prices so low that as many people as possible will be able to afford them.”
3. Values
Organizational values are guiding principles that reinforce a company’s culture, decision-making processes, and behavioral and moral standards.
Values represent the core beliefs and attitudes that define the organization’s identity and ethics.
The main role of values is to create a sense of identity and unity within the organization. They align individual and organizational goals, building commitment and motivation among employees.
Values also contribute to the organization’s public image and can be a powerful tool for attracting like-minded employees and customers.
Key characteristics of effective value statements include:
- Alignment with the organization’s mission and vision
- Clarity and specificity
- Relevance to both employees and stakeholders
- Integration into the organization’s Code of Ethics
- Flexibility to accommodate diverse perspectives
- Ability to guide behavior and decision-making
Examples of Great Organizational Values:
Microsoft – “Innovative Technology | Diversity and Inclusion | Corporate Social Responsibility | AI Development | Trustworthy Computing”
LEGO – “Imaginative Play | Creativity | Joyful Enthusiasm of Children | Learning Through Curiosity”
Netflix – “The Dream Team | Prioritize People over Process | Uncomfortably Exciting | Great and Always Better”
Adidas – “Courage | Ownership | Innovation | TeamPlay | Integrity | Respect”
The Importance of Putting Vision, Mission, and Values Together
A company’s vision, mission, and values (VMV) must be interconnected to drive business success. Those that align these elements ensure that their vision provides a future-oriented framework, their mission outlines concrete goals and implementation strategies, and their values reinforce their behaviors and decision-making.
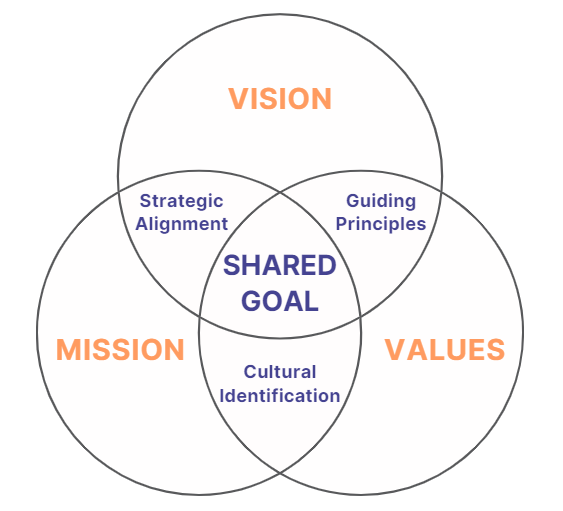
- Strategic Alignment: the long-term goals (vision) are supported by the organization’s current objectives and actions (mission).
- Guiding Principles: the aspirational future state (vision) is shaped by the core principles and beliefs (values) that define how the organization operates.
- Cultural identification: the day-to-day operations and purpose (mission) are grounded in the organization’s fundamental beliefs and ethical standards (values).
If VMV statements are not well-aligned, they will confuse the employees and stakeholders, leading to frustration, internal conflicts, and a weakened organizational culture.
Three key questions to ask when writing VMV statements to ensure interconnection are:
- Does our vision provide a clear, inspiring future state that aligns with our mission and values?
- Does our mission outline concrete goals and strategies that support our vision while embodying our values?
- Do our stated values underpin both our vision and mission, providing clear guidelines for behavior and decision-making across all levels of the organization?
By addressing these questions, companies can create a powerful, interconnected VMV framework that drives marketing success and overall business performance.
Read More: Use Gamification In Marketing – Uncover The Secret Behind Duolingo’s Success
How To Write Clear Vision, Mission, and Value Statements?
Step 1: Define your brand purpose
- Reflect on your organization’s core reason for existence
- Identify your unique selling proposition and long-term aspirations
- Consider your organization’s impact on society and stakeholders
- Align your purpose with market needs and organizational capabilities
Step 2: Understand your stakeholders’ values
- Identify key internal and external stakeholders
- Conduct surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gather input
- Analyze stakeholder expectations, needs, and priorities
- Identify common themes and values across stakeholder groups
Step 3: Define and Draft
- Vision (30-40 words): Create a clear, inspiring future state, and ensure it follows the above key characteristics.
- Mission (50-100 words): Outline concrete goals and strategies, address key questions about purpose, uniqueness, and objectives, and ensure it’s clear, specific, and actionable.
- Values: List 3-5 core principles relevant to employees and stakeholders to guide behavior and decision-making.
Step 4: Communicate and Implement
- Share VMV statements across all organizational levels
- Integrate VMV into training programs, policies, and decision-making processes
- Regularly reinforce VMV through internal and external communications
- Encourage employee feedback and participation in living the VMV
- Periodically review and update VMV to ensure continued relevance and effectiveness
Understanding the firm’s vision, mission, and values guides the management to more sustainable decisions and inspires stakeholders toward a shared purpose.
By clearly defining what your company aspires to achieve (vision), its core purpose and objectives (mission), and the principles that guide its behavior (values), you can differentiate your organization, align internal and external stakeholders, and drive long-term success.
[wpforms id=”411″ title=”true” description=”true”]
Academic Sources For The Blog:
Roblek, V., and Meško, M. (2018) The importance of vision and mission for organizational development and growth. Conference: Challenges of globalization in economics and business.
Kirkpatrick, S.A. (2017) UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF VISION, MISSION, AND VALUES IN THE HPT MODEL. Performance Improvement. 56 (3).
Sy Chu
As an analytical and creative marketing enthusiast skilled in customer analysis, content research and brand management, my passion is help businesses gain insights into their brand and marketing strategies to drive impactful outcome to their success.
