What is Competitive Positioning?
‘Competitive positioning is the firm’s value propositions that can satisfy customers’ needs better than other alternatives. Competitive positioning sets the firm apart from others while still maintaining its conformity to the industry standard.’
Define Competitive Positioning from Market Orientation
First, let’s debunk what market orientation is. Marketing orientation achieves organisational objectives by understanding and anticipating customers’ current and future needs, then along with various departments, engaging in activities that can satisfy these needs better than competitors.
Instead of the past focus on making and selling average stuff for average people, the concept of market orientation is a sense-and-respond philosophy. As Philip Kotler has said, the job is not to find the right customers for your product but to find the right products for your customers.
From this perspective, competitive positioning is a brand’s value proposition that includes all the benefits the brand promises to give customers. In other words, competitive positioning helps the brand differentiate itself and become a must-visit destination when the market searches for a specific solution to their needs.
Define Competitive Positioning from Competitor Orientation
While market orientation is more market-driven, focusing on understanding customer needs, competitor orientation flips the script and analyzes existing players in the marketplace to refine the brand’s competitive positioning.
Overall, this concept revolves around benchmarking competitor offerings, identifying both points of parity (shared values) and points of difference (unique selling propositions – USP). Hence, competitive positioning is a set of attributes that not only reach the standards of the industry but also emphasize differentiating factors to deeply resonate with the target audience.
How to Identify a Competitive Positioning?
Having recognised the importance of competitive positioning in marketing strategy, now I want to introduce you to a step-by-step process of identifying one, which is proposed by Hooley et al. (2020) in ‘Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning‘ book (see Figure below).
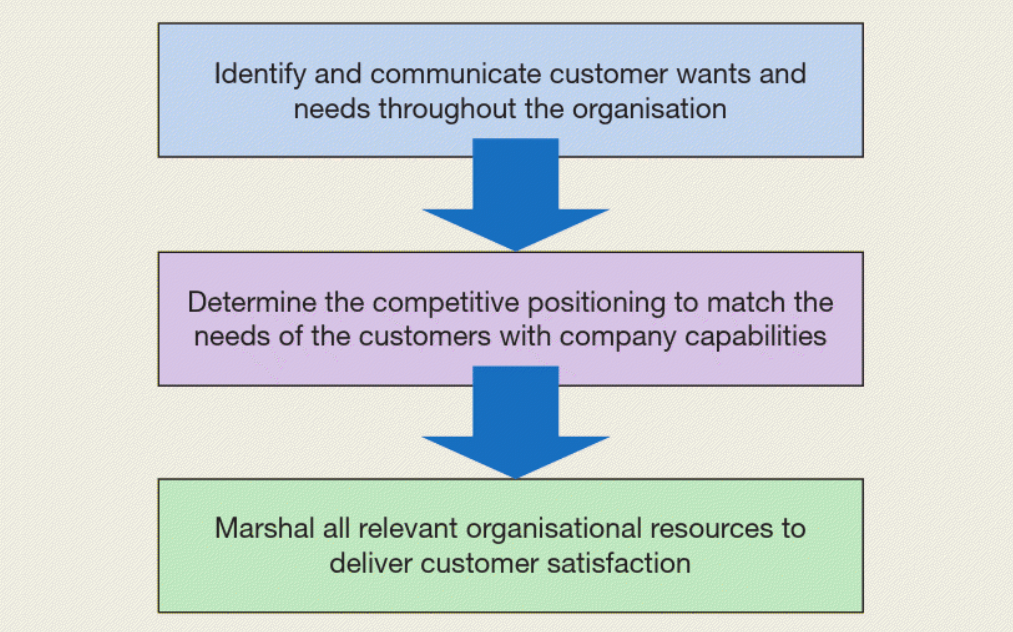
Stage 1: Identify current competitive positioning by understanding the Marketplace
In this section, I will delve into 3 primary components of the marketplace: customers, competitors, and the external environment.
1. Customer Segmentation
Understanding your customer base is crucial for effective competitive positioning. In short, customer segmentation is an act of dividing your target audience into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, interests, and values. The common sources of information for customer segmentation are demographics, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral.
• Demographics: this includes basic and easy-to-collect information related to the profile of customers such as age, income levels, education, and family status.
• Geographics: this aspect segments customers by their locations, climate variations, or even their languages to create seasonal products relevant to specific places.
• Psychographics: these depict the insights of customers, including their lifestyles, values, and personality traits. Psychographics are the hardest pieces of information to collect but they are undeniably the most important factors to identify the firm’s competitive positioning.
• Behaviorals: some brands can segment their consumers by past purchases or usage situations to recommend related products, and personalise promotions.
Overall, effective segmentation often involves combining multiple factors. By effectively segmenting the customer base, the firm can develop targeted competitive positioning strategies that resonate with the select groups, ultimately giving it a sustainable advantage in the marketplace.
2. Competitor Analysis
Gaining knowledge of key competitors’ strengths and capabilities is very important for the success of a competitive positioning strategy. Competitor Analysis involves deciding which competitors to benchmark against and using the positioning map to understand the firm’s current and future positioning strategies.
First, let’s identify direct and indirect competitors in the marketplace. While direct competitors are those offering similar products or services to the same group of audience, indirect substitutes are firms that satisfy the same needs as yours with different offerings or value propositions. For example, a streaming service like Netflix competes not only with other streaming platforms but also with traditional TV channels or video game subscriptions.
Having identified key rivals, it’s important to visualise your competitive landscape using a positioning map. This tool plots competitors based on two key dimensions, typically chosen from factors like price, quality, features, or target audience. By positioning itself on the map relative to competitors, the firm can identify its unique value proposition and potential niches in the market (See figure below).
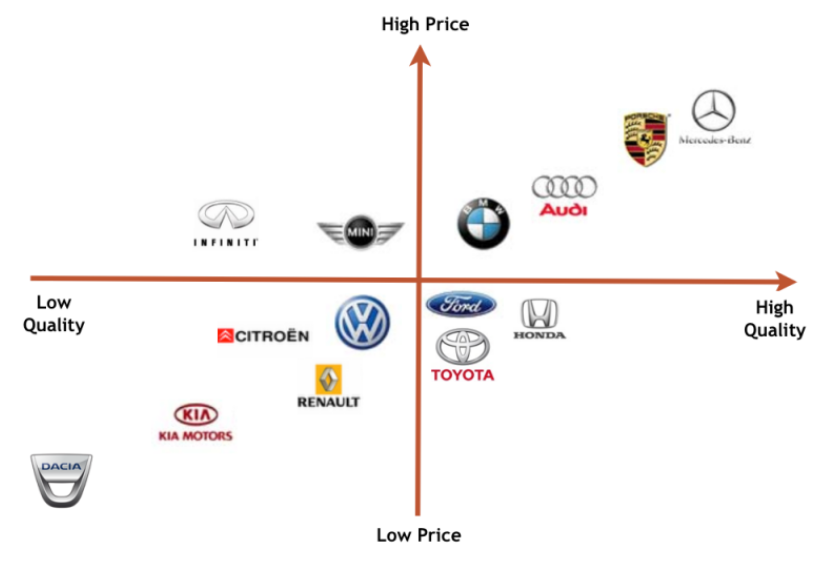
3. External Analysis (PESTEL framework)
The backbone of a successful marketing strategy and competitive positioning is the firm’s ability to adapt to the ever-evolving nature of external factors, which are formulated by governments and authorities, totally out of control.
Now, let’s delve deeper into each element of an external analysis using the PESTEL framework first proposed by Professor Francis Aguilar in 1967.
3.1. Political and Economic Analysis
In the increasingly complex and interconnected global landscape, understanding economic indicators and political risks is key to a company’s competitive positioning strategy.
Globalisation, characterised by the seamless flow of goods, services, and information across borders, has given us new opportunities for market growth. With the emergence of trade agreements like NAFTA, the EU Single Market, and other multi-lateral agreements, companies nowadays capitalise on tariff reductions and access to new markets.
Besides, the rise of middle-class citizens in developing countries, especially BRIC areas (Brazil, Russia, India, and China) has opened new opportunities for leading corporations to compete and gain their market share by tailoring product offerings and positioning strategies to new consumption patterns. For example, 40% of middle-class citizens worldwide come from China, making it a lucrative market for luxury brands. Since 2022, China has become the second-largest personal luxury goods market, changing the entire luxury industry.
3.2. Social-cultural Analysis
Covid 19 pandemic has resulted in several changes to our society. Among them, shifting lifestyles and living patterns play a significant role in the competitive marketplace. From a shift to remote work and the rise of the middle class to thriving multicultural communities on social media, companies nowadays have to work harder to anticipate their customers’ evolving needs and wants.
By incorporating these social factors into your competitive positioning strategy, firms can develop offerings that resonate deeply, ultimately securing their sustainable competitive advantage in the marketplace.
3.3. Technological Development
Personally, technology is the most vital factor when it comes to securing a competitive position. For this section, I will introduce you to 3 areas of technology that may help your business identify both current and future positioning.
• Digital Transformation: without a doubt, businesses across industries are undergoing a digital transformation, embracing automation, cloud computing, and online platforms. This development brings about new opportunities to develop sustainable advantage and positioning for companies to provide omnichannel experiences, which integrate between online and offline touchpoints.
• AI Applications: AI is revolutionising our world. For the last couple of years, AI-based marketing strategy has been developed to help companies compete in every single aspect, from personalised experience, automated email, and ad marketing, to Chatbots and Virtual assistants.
• SaaS (Software as a Service): the rise of Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions has disrupted traditional software models. From customer relationship management (CRM) to marketing automation, SaaS offers scalability, affordability, and access to cutting-edge technology. This is why the global SaaS market reached $261.15 billion in 2022.
To conclude, I want to reconfirm that understanding the marketplace where you compete is extremely important to how you define competitive positioning for your business.
Stage 2: Determining competitive positioning to meet customers’ needs
1. Assess the current resources and capabilities
Grabbing the picture of the marketplace will not guarantee a sustainable competitive position unless the company leverage its expertise and existing resources to offer superior values to customers than others. Let’s capture some key factors that constitute the importance of assessing organisational resources before deciding which competitive positioning strategy to go for:
• Understand Advantageous Resources: Not all resources create equal value for customers. Some firms leverage brand reputation as their competitive positioning, some rely on the excellence of customer services and customer relationship management. Hence, understanding who you are can help you identify unique and hard-to-replicate values to offer customers (I’ll explain more below).
• Create a Sustainable Competitive Advantage: Building an advantage to compete is not enough. You have to ensure that it is sustainable by creating barriers to imitation. Thus, some basic questions must be answered such as: Can others do what you’re doing? How much resources does it take them to do what you’re doing?
2. Decide on your competitive positioning strategy
Now, let’s decide which competitive advantage to pursue. Here, I will use the model introduced by Michael Porter in his genius ‘Competitive Advantage’.
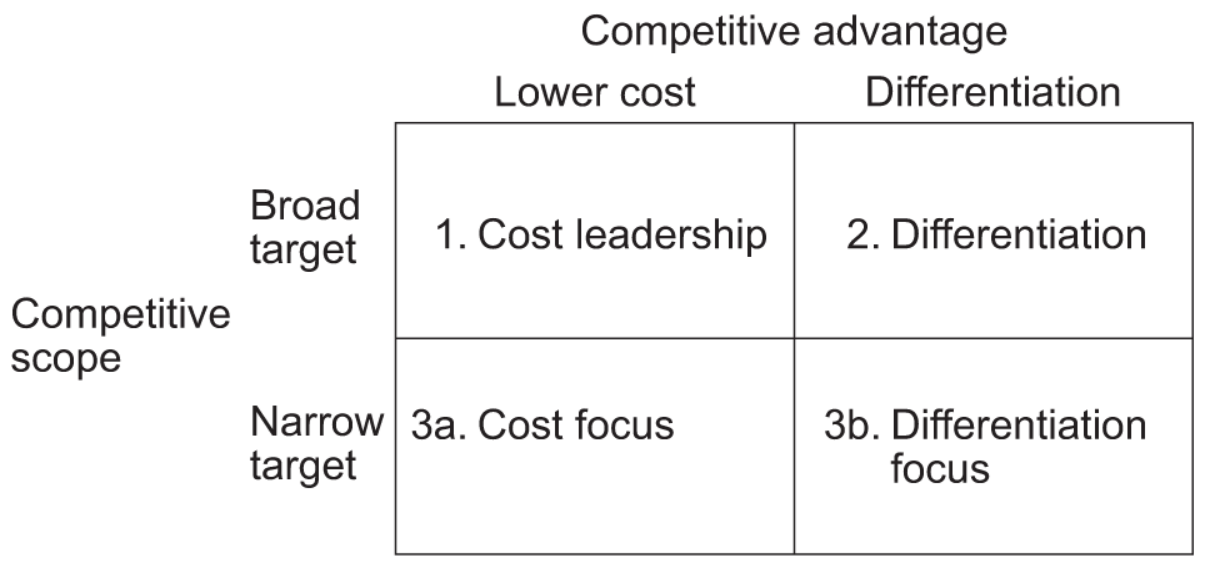
2.1. Cost leadership
One way to sustain your competitive positioning is to dominate through efficiency and position yourself as the cheapest. In other words, this strategy hinges on achieving the lowest overall cost of production and delivery compared to your competitors within the marketplace.
Cost leadership can be achieved via economies of scale, where producing large volumes lowers costs per unit, or via superior operations and lean management practices.
At present, the retail giant Walmart is employing this positioning strategy very well. Specifically, the company leverages its massive scale, efficient supply chains, and meticulous cost-control measures to minimise its cost structure, offering everyday low prices for its customers without spoiling customer relationships.
2.2. Differentiation
In the red ocean full of blood, differentiation allows companies to rise above the noise and discover their blue oceans. In short, a differentiation strategy focuses on creating products or services that are uniquely valuable compared to offerings from competitors.
I will take Apple as a shining example of this positioning route. Through innovative design, intuitive user experiences, and a carefully cultivated brand image, Apple has created products that customers are willing to pay a premium for. This premium differentiation allows them to command higher margins and maintain a loyal fanbase despite facing competition from other smartphone and technology manufacturers.
2.3. Cost Focus
Again, not all markets are created equal. With a cost focus strategy, the firm targets a specific niche market and strives to be the most affordable provider within that segment.
Some airline brands have mastered this strategy. For standard class, they cater to the budget-conscious segment of the air travel market, offering no-frills fares, streamlined services, and onboard amenities.
2.4. Differentiation Focus
What if you can combine the power of differentiation with the focus of a niche market? That’s what the differentiation focus strategy offers. Here, the company creates unique value propositions specifically tailored to the unique needs and preferences of a particular customer segment. This strategy requires developing products or services that directly address their pain points and desires.
This positioning route works pretty well in the luxury sector. Luxury car manufacturers like Rolls-Royce only cater to a small but wealthy and lucrative segment by manufacturing vehicles with exceptional craftsmanship, highly personalised features, and exclusive driving experience.
Read my latest update on Sustainable Marketing at: What is Sustainable Marketing? Definition, 4Ps Strategy, Trends & Challenges
Final Stage: Monitor Your Current Competitive Positioning
I’ll keep it concise and clear for this last stage. As we’re living in such an ever-evolving world of business, the current positioning today may not be profitable or relevant to customers’ needs tomorrow. That’s why actively monitoring your competitive positioning is the final and crucial stage in identifying and maintaining a sustainable edge.
1. Track Internal Performance
• Continuously evaluate key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with your chosen strategy. Are you achieving your cost leadership goals? Is your differentiation strategy resonating with customers? Besides, it’s important to use data to gauge progress and identify areas for improvement.
• Monitor resource capabilities: Regularly assess your resource strengths and weaknesses. Are your cost-reduction initiatives effective? Is your R&D keeping pace with industry advancements?
2. Anticipate External Environment
Personally, the firm should always stay ahead of evolving industry trends, customer preferences, and technological innovation. These factors can either pose threats or unlock opportunities.
3. Conduct Regular Customer Analysis
Finally, your competitive positioning must be relevant to customers’ needs and wants. Hence, it is recommended that the firm should gather customer feedback and regularly solicit customer insights through surveys, interviews, and social media monitoring. Understanding their evolving needs and perceptions helps ensure the strategy remains relevant and superior in addressing their pain points.

[wpforms id=”411″ title=”true” description=”true”]
Academic Sources for this blog:
Porter, M.E. (2004) Competitive Advantage. New York ; Free.
Hooley, G. J., Nicoulaud, B., and Rudd, J.M. (2020) Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning, 7th edition. Harlow, England: Pearson.
Sy Chu
As an analytical and creative marketing enthusiast skilled in customer analysis, content research and brand management, my passion is help businesses gain insights into their brand and marketing strategies to drive impactful outcome to their success.
